Robotic surgery is a fairly recent addition to the medical world and by itself is showing great promise for greater success rates and possibilities to perform surgeries previously thought unrealistic. It is one of, if not the, most advanced applications of technology in healthcare. These surgical robots assist surgeons in performing complex procedures with unprecedented precision, dexterity, and control, leading to numerous benefits for patients and healthcare providers alike. Now with the introduction of ever more powerful artificial intelligence, the amalgamation between the two shows even more potential.
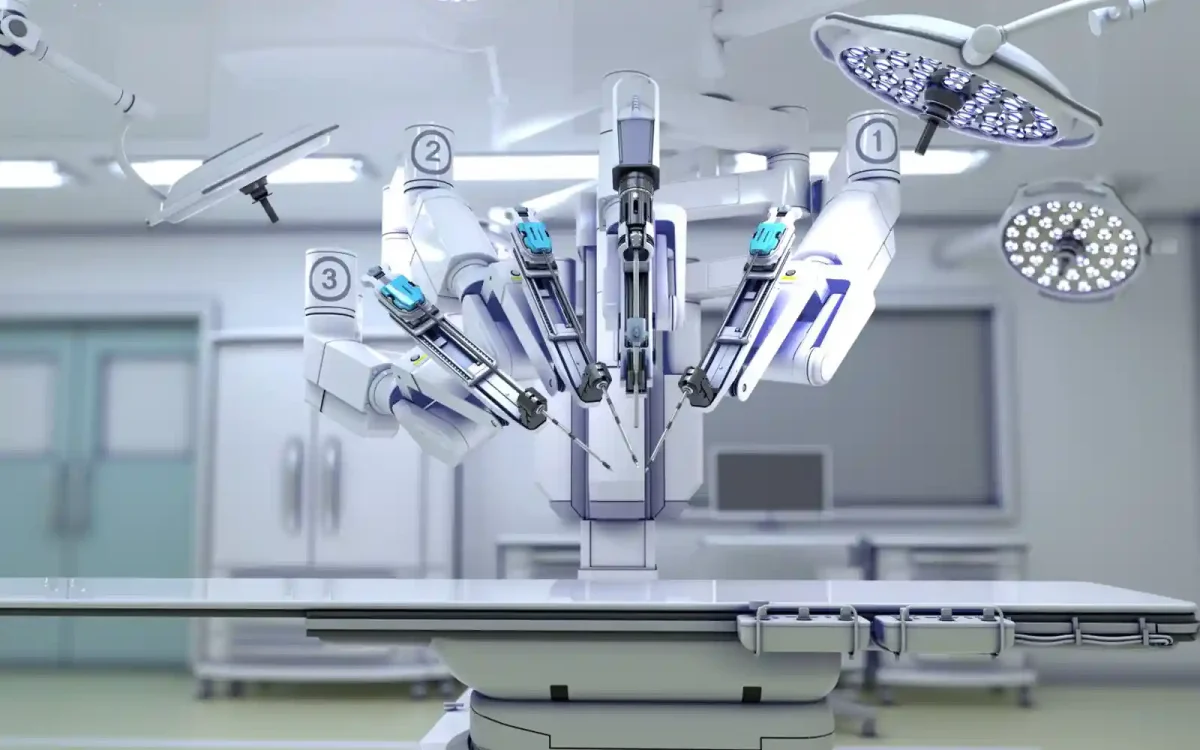
Robotic surgical systems have been used since 1985, but since then they have become substantially more precise. Systems such as the da Vinci Surgical System leverage AI to provide enhanced precision during operations. Though artificial intelligence is not yet trusted enough to have full control over a surgery and a patient’s life, these robots instead translate and scale down the surgeon’s hand movements into smaller, more precise actions of tiny instruments inside the patient’s body to the millimeter. This level of precision is particularly beneficial in delicate surgeries where human hands might be too large or unsteady to perform minute and intricate maneuvers safely.
AI-powered surgical robots offer far greater dexterity than human hands, capable of rotating and bending in ways that a human wrist cannot. This increased range of motion allows surgeons to operate in hard-to-reach areas with more control. Enhanced visualization tools, including 3D high-definition imaging, provide surgeons with a clearer view of the surgical site, further improving the accuracy and effectiveness of the procedures. Various videos have been recorded of medical professionals creating origami paper cranes smaller than pennies, demonstration the precision of these systems.
One of the main benefits of robotic surgery is the minimally invasive nature which often results in smaller incisions, and shorter recovery times for patients. Reduced trauma to the body means patients experience less pain, lower risk of infection, and quicker healing. This swift recovery not only benefits patients by allowing them to return to their daily lives sooner, but also reduces hospital stays and associated healthcare costs.
The translation of robotic surgery using AI allows for greater precision and control resulting in very few surgical complications. In addition to this, AI can assist in planning the surgery by simulating the procedure beforehand, identifying potential issues, and optimizing the surgical approach. During the operation, AI algorithms monitor the patient’s vital signs and provide real-time feedback to the surgeon, helping to prevent complications before they arise. All of these proactive steps result in safer surgeries with better outcomes as well as providing the patient reassurance.
The combination of precision, dexterity, and control provided by that of AI-powered robotic surgery leads to improved surgical outcomes. Higher accuracy in performing delicate procedures reduces the likelihood of errors and enhances the overall success rates of surgeries. Patients benefit from more successful operations, less postoperative pain, and better long-term health results. This is especially important regarding procedures with low success rates such as open-heart surgeries to increase those chances as well as decreasing those extremely long recovery periods.
Overall, AI-powered robotic surgery is not just transforming but rewriting the rules in the field of surgery, offering numerous advantages including greater precision, improved dexterity, shorter recovery times, reduced complications, and better surgical outcomes. As this technology continues to advance, these surgeries will become better and the role of AI in surgery is likely to expand, further revolutionizing the way complex procedures are performed and enhancing the quality of patient care.