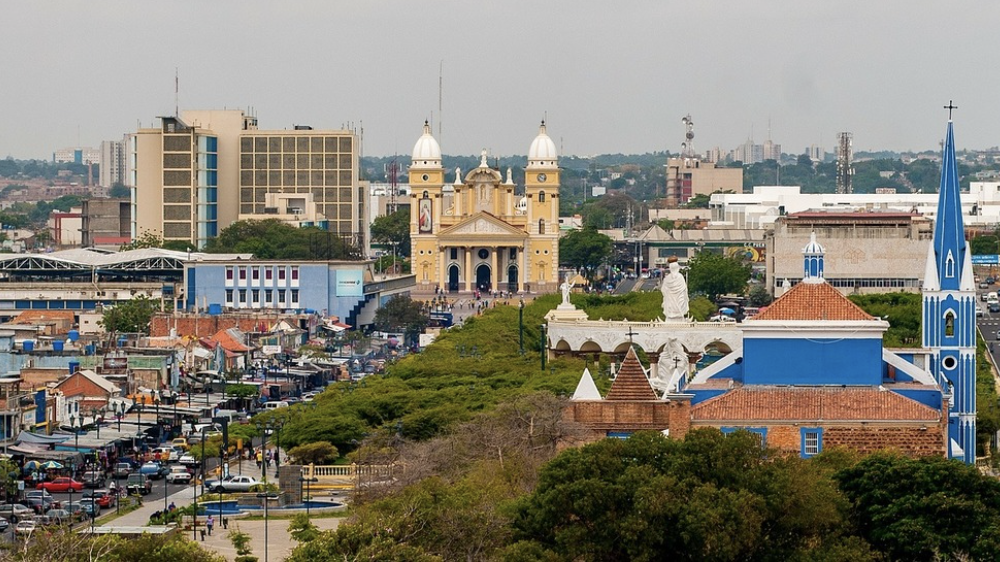
In 1814, the British purchased Guyana from the Netherlands and ruled over Guyana until 1966. Since 1841, Guyana and Venezuela have had a border dispute over the Essequibo region which is located within Guyana’s territorial boundaries recognized by the United Nations and other major world powers. However, Venezuela has claimed the region as their territory. Today, the strife between the two countries has intensified because of the large oil deposit in the region. Researchers have continued to be in discussion over if the dispute will transition into a full scale war. In my opinion the ongoing border dispute will become a war because of the region’s economic incentives along with other social and political factors.
Firstly, the countries are mainly fighting over the oil deposit in the region as the resource is vital to their economy. It’s important to establish context into the Essequibo region, in 2015 the dispute reached its highest level of intensity when a major oil deposit was discovered in the region by the Exxon-Mobil consortium. Consequently, the discovery sparked interest from Venezuela because of the economic wealth that this major oil find can provide. However, within recent years Guyana has moved aggressively to extract this valuable oil find which has further inflamed the war of words with Venezuela. From Guyana’s exploitation of the deposit, the country has generated approximately 1 billion a year from it and has expanded its economy by 60% within the first half year of exportation of the oil.
Secondly, increased military support of both countries has furthered pointed the conflict into war. Iran publicly stated their support for Venezuela in the dispute by providing them with military equipment and other resources. However, in May 2024, U.S. fighter jets were seen flying over a nearby base in Georgetown (capital of Guyana) and many began to speculate that the U.S. is continuing its backing of Guyana especially given that Exxon is a major US corporation. To further this notion, the U.S. committed $900 billion dollars to the funding of the Caribbean Basin Initiative (CBSI) and Guyana is one of the nations benefiting from the initiative. Guyana is likely to use their share of the funds to improve their infrastructure and military enforcement. With both countries backed by powerful nations we are likely to see increased tensions between the countries.
Finally, there is a great deal of national fervor within both countries which has contributed to the discord intensifying. The countries have engaged in light skirmishes on and off over the disputed area since 1898 even when Guyana was still a British colony. In December of 2023, the Guyanese president, Ali stated that Guyana will refuse to back down to Venezuela. His words are a reflection of the extensive and layered history that is attached to the conflict and the sense of national pride that Guyana has for the Essequibo region which is the largest region in Guyana.
Ultimately, the border dispute is a classic tale of a smaller country being forced to defend its territorial area against a larger more militarily powerful neighbor. It is also important to note that past colonial trades and actions involving powerful European nations have contributed to this ongoing dispute. Lastly, both countries are likely heading for war due to the immense economic benefits that can be gained from the massive oil deposits discovered in the Essequibo region.